PROLINE Alkaline Phosphatase FS IFCC 37°C
| Catalogue Number | R1 Reagent Volume | R2 Reagent Volume |
| 10441 99 10 920 | 4 x 34 mL | 4 x 10 mL |
| 10441 99 10 921 | 4 x 21 mL | 4 x 6 mL |
| 10441 99 10 190 | 4 x 20 mL | 4 x 5 mL |
| 10441 99 10 180 | 4 x 20 mL | 4 x 5 mL |
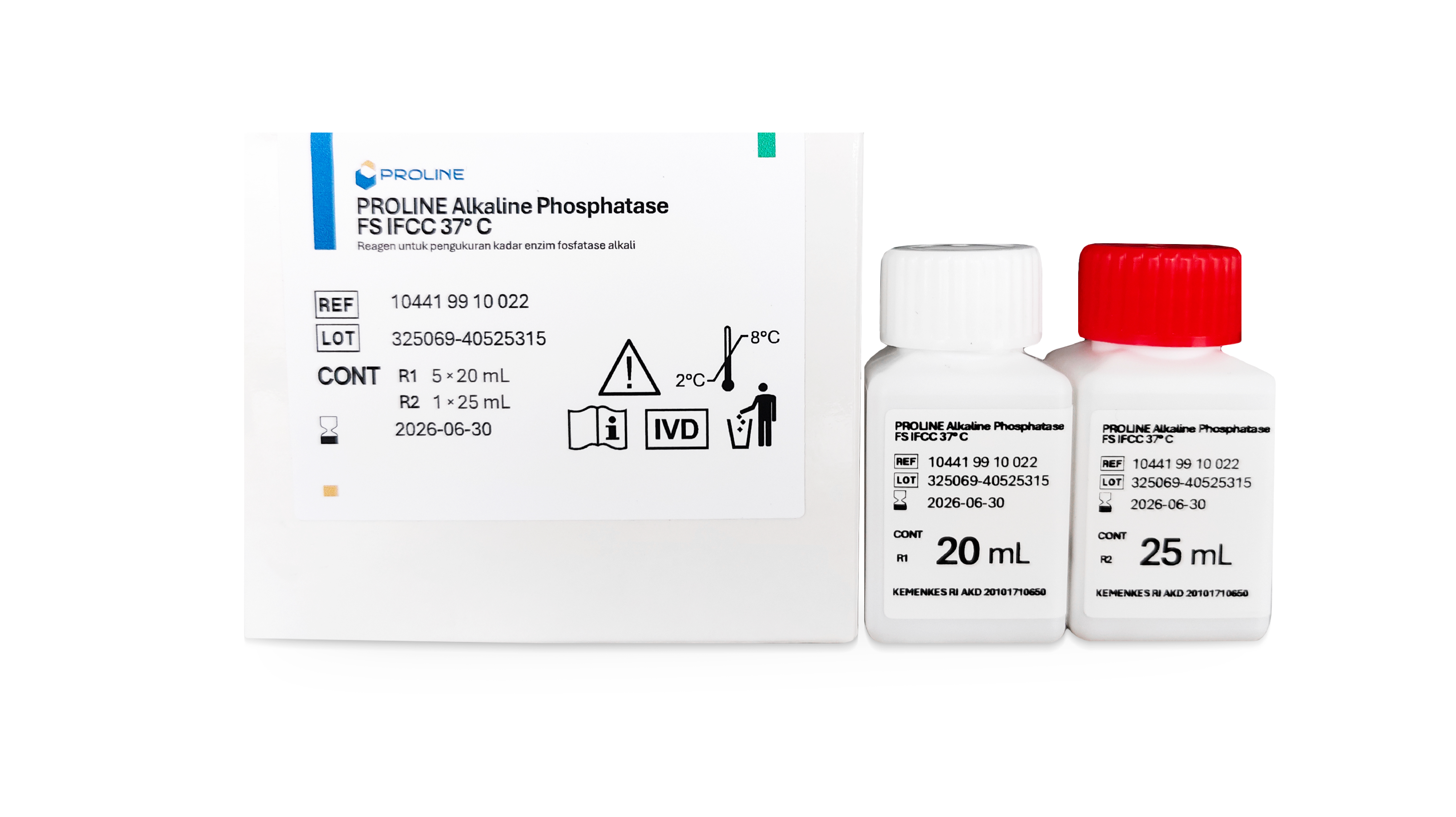
| 10441 99 10 022 | 5 x 20 mL | 1 x 25 mL |
| 10441 99 10 965 | 6 x 25 mL | 6 x 6 mL |
| 10441 99 10 914 | 6 x 60 mL | 6 x 15 mL |
| 10441 99 10 951 | 6 x 36 mL | 6 x 9 mL |
| 10441 99 10 591 | 4 x 60 mL | 4 x 15 mL |
| 10441 99 10 027 | 2 x 100 mL | 2 x 25 mL |
In vitro diagnostic reagent for quantitative examination of alkaline phosphatase (AP) enzime activity in human serum or heparin plasma using photometric measurement methods.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme found in various human body tissues, particularly in the liver, bones, kidneys, and intestines. This enzyme functions optimally in an alkaline environment and serves to catalyze the release of phosphate groups from molecules such as nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids.
In the body, ALP has several physiological functions, including phosphate metabolism, bone mineralization, and tissue regeneration. In the skeletal system, ALP plays a crucial role in the maturation of osteoblasts and bone formation. Additionally, ALP helps break down phosphate-containing molecules so they can be absorbed by the body. In the liver, ALP is involved in lipid transport and detoxification. Changes in ALP activity can be a response to inflammatory processes or metabolic disorders.
Abnormal levels of ALP may be an indication of disease. Elevated ALP levels are commonly found in liver conditions such as cholestasis, hepatitis, and cirrhosis, as well as in bone disorders like Paget's disease, osteomalacia, and bone cancer. On the other hand, low ALP levels may occur in cases of malnutrition, hypophosphatasia (a rare genetic disorder), or deficiencies in zinc and magnesium. Therefore, ALP level testing is often conducted as part of laboratory evaluations for hepatobiliary and bone disorders.
Kinetic photometry test, referring to the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) [modif.]
- Ready-to-use liquid reagent (open-system) without reconstitution
- Excellent linearity and stability performance
- Available in MPK (Multi-Purpose Kit) and dedicated kit
- Compatible with >65 brands of manual and automated clinical chemistry analyzers
| Sample type | Human heparin serum or plasma |
| Measurement range | 2.64 U/L - 1400 U/L |
| Analysis wavelength | Hg 405 nm, 400 – 420 nm |
| Analysis mode | Kinetics |
| Reagent volume used (analyzer manual) | R1: 1000 µL ; R2: 250 µL |
| Sample volume used (analyzer manual) | 20 µL |
| Storage temperature | 2 – 8 °C |
| Open vial stability | 12 months |
| Expiration date | 15 months |
| Reference Range: | ||
| g/dL | μmol/L | |
| Adult | ||
| ≤ 60 years | 3.5 - 5.3 | 507 - 753 |
| > 60 years | 3.4 - 4.8 | 492 - 695 |
| > 70 years | 3.3 - 4.7 | 478 - 681 |
| > 80 years | 3.1 - 4.5 | 449 - 652 |
| > 90 years | 3.0 - 4.5 | 434 - 652 |
| Child | ||
| Newborn | 3.5 - 4.9 | 507 - 710 |
| 1 years | 3.6 - 5.0 | 521 - 724 |
| 2 - 20 years | 3.7 - 5.1 | 536 - 738 |
- Alkaline Phosphatase Reagent
- Doos
- Kit insert
- Reagents bottle
- Kit Insert PROLINE Alkaline Phosphatase FS IFCC 37°C (10441 01 – Okt 2024/02)
- Millán, J. L. (2006). Alkaline phosphatases: structure, substrate specificity and functional relatedness to other members of a large superfamily of enzymes. Purinergic Signalling, 2(2), 335–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-005-5435-6
- Ramasamy, I. (2014). Recent advances in physiological bone turnover markers. Clinica Chimica Acta, 437, 213–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.07.006
- Peters, M. D., et al. (2016). Diagnostic performance of alkaline phosphatase for detecting liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open, 6(6), e010058. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010058
- Brochure : INA
- Liver Disease
- Bone Metabolism
Contact our team to find out more product information and ordering
- Telp : +62 21 8984 2722
- WhatsApp : +62 815 1359 2626
- Email : marketing@proline.co.id
Contact our Technical support team for further assistance with product specifications, services and other technical documents.
- Telp : +62-21-8984-2722
- WhatsApp : +62-817-9324-884
- Email : technical.support@prodis.co.id
